5 Ways to Stand Out in SERPs and Increase Organic CTRs
Higher rankings should lead to traffic increases, but what do you do when climbing rankings don’t deliver increased clicks? Ranking on page one for target keywords is a first step, but it remains essentially meaningless if users aren’t clicking on your result.
If you’re struggling with low organic click-through rates (CTRs), your site’s appearance in search results may not be standing out from the competition. It’s possible that they don’t cater to user intent, or they may simply be less exciting than the other results on the page.
One way to improve click-through rates is to optimize how your content displays on search engine results pages (SERPs). By creating search results that stand out on the page you can drive more traffic to your site, and the increased engagement may even earn you higher rankings.
Get Started by Identifying Underperforming Pages
The first step in optimizing search results is to find underperforming pages. This information can be found in Google Search Console by:
- Expanding “Search Traffic”
- Clicking on “Search Analytics”
- Selecting the “Pages” radio button
- Selecting the checkboxes for “CTR” and “Position”
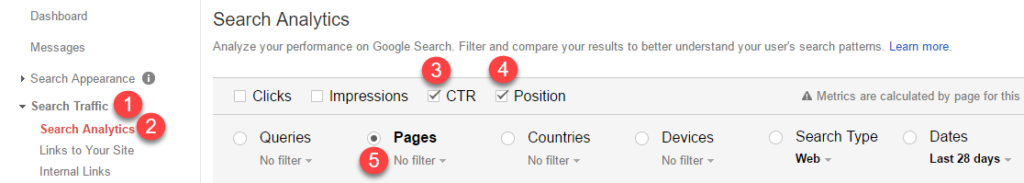
Focus on pages with average positions between one and 10, and then look at the CTR values for each. Ultimately, you’ll need to decide what CTRs are acceptable. One way to decide is to compare CTRs of different pieces of content that are ranked in the same position.
If five results appear in position one—three with CTRs of 30% and two with CTRs of 15%—the two pages with 15% CTR need to be optimized.
If there aren’t enough pages and data to make this determination by comparison, refer to average CTRs by position:
- Position 1: ~30% CTR
- Position 2: ~17% CTR
- Position 3: ~12% CTR
- Positions 4-6: ~5-10% CTRs
- Positions 7-10: ~2-5% CTRs
Compile a list of pages with low CTRs. These are the pages with results that need to be optimized.
1. Craft Compelling SEO Page Titles
Back when Google served results mostly by matching character strings, it was crucial to include exact-match keywords in SEO titles. This led many sites to format titles like this: Search Engine Optimization | How to Optimize Your Site for Search. The titles were clear, but usually very boring and redundant.
Today, 53% of the top 20 search results use keywords in their SEO titles. Google is not dependent as it used to be on matching characters in title tags to serve results. Instead, it uses body text, sub headers, latent semantic indexing, and engagement signals to match results to queries.
And RankBrain is constantly reevaluating and adjusting which ranking factors are more important for which queries. Keywords are more important in some industries, and for some content topics, than others.
There are several best practices to consider when writing titles for search result display:
- Check with RankBrain – Conduct a depersonalized search for targeted keywords, and study the SERPs to see if keyword matching is important. If the exact keyword appears in many or most of the titles in organic results, then RankBrain might be prioritizing it. If you see a lot of synonyms and related terms, matching keywords isn’t as important.
- Length – If SEO titles are too long, Google will truncate them with an ellipsis. To avoid this, most SEOs recommend a maximum of 70 characters. Profound Strategy’s standard best practice is 55 characters, however, because Google counts pixels (not letters) and because it frequently emboldens words that match the user’s query.
.
If your content management system automatically adds a separator and brand name at the end of SEO titles, make sure to account for those characters in the total, or add that information yourself instead of having it auto-appended. Conversely, use the character limit to create suspense.
- User Intent – When users conduct a search, they’re asking a question. Make sure your SEO title makes it immediately clear what answers the content provides. Clever or suspenseful titles are great, but if they don’t make the subject matter of the content obvious, no one will click them.
- Audience – Which persona is each piece of content written for? Consider addressing that persona in the SEO title. “How to Measure Content Marketing Results” could be made more compelling by addressing a specific audience. If the audience is individual contributors, the title “How to Prove to Your Boss That Content Marketing Is Generating Revenue” is much more compelling.
- Brackets – Highlight benefits of content briefly using brackets in SEO titles, or use brackets to signify the type of content the user can expect to find on the page.
.
For pages with high rankings but low CTRs, consider updating SEO page titles to make them more compelling. Then, measure the results to determine if click-through rates improve.
You can also use Twitter to test possible headlines. Since it’s not as frowned upon on Twitter to post multiple updates that link to the same content, play around with different titles, and post them to Twitter and see which earn the highest engagement rates.
2. Write Enticing Meta Descriptions
Well-crafted meta descriptions are another opportunity to inspire clicks. Meta descriptions are an extension of page titles, providing a promise to users about what they can expect to find after clicking a result. And because they aren’t ranking factors, they can be used solely to entice users to click on results.
Effective meta descriptions:
- Do not exceed 160 characters. Like SEO titles, Google will truncate meta descriptions that are too long. If your content management system automatically prefaces meta descriptions with a publication date, make sure to account for the characters the date will use (~16) in the overall character count.
- Create a longer meta-substitute in the text. Occasionally, Google will allow for a longer, three to four line meta description if it believes that a longer snippet of the content provides a better answer to user intent. Longer meta descriptions stand out because they take up more real estate on the page. Take time to optimize content to create concise definitions, or use H2 tags to list step-by-step instructions or items in a list.
.

- Don’t repeat the SEO title. Provide additional information that entices users to click.
- Use advertising copy. While it might be tempting to simply cut and paste a line of body text into the meta description field, this method is not ideal. The best meta descriptions use the best practices of advertising copy—they’re persuasive, descriptive, and include a CTA.
Unfortunately, there’s no guarantee that Google will display the meta description you’ve written. Google recently admitted that defined meta descriptions are the fall-back, not the default, for what gets displayed on a SERP. That means the search engine is looking for appropriate pieces of on-page content first, and only using the meta description you specify if it can’t find good enough answers on the page.
Of course, this is no great surprise:

A search for “digital marketing analytics” produces this auto-generated description.
![]()
Google uses the first line of the specified meta description, but it chooses another section of the text to show a usage of the word “analytics” in the content.
First, make sure to include a variety of meta-description-worthy sentences and short paragraphs in the content for Google to pull out.
Alternately, including keywords in meta descriptions may increase the likelihood that Google will use the meta description you provided instead of generating its own. Additionally, Google displays matching keywords in meta descriptions in bold, which helps results stand out.
3. Customize URLs
While URLs are less important than compelling and descriptive SEO titles and meta descriptions, they do display in search results so they should reflect the content of the page. Page URLs factor into searchers’ perceptions of relevance: descriptive URLs get 25% more clicks than non-descriptive URLs.
If you’re using WordPress or another content management system that auto-generates numeric URLs, make sure to update the URL before publishing to make it more relevant to the content.
If you need to update URLs for already-published pages, make sure to have a plan in place for redirects. Updating the URLs of pages may be a simple task, but it can create cascading negative impacts if you neglect to implement 301 redirects after updating URLs.
4. Use Structured Data
Marking up pages with schema or microdata can result in more visual, detailed, or longer search results. Some examples of expanded results that can display when using markup include:
- Videos – Pages that include a video can display a thumbnail in search results. To have a video thumbnail display, ask a developer to add structured data to pages that include videos. Or if you use WordPress, the Yoast Video SEO plugin provides a simple way for non-technical users to add structured data markup to videos.
.
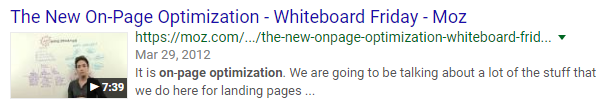
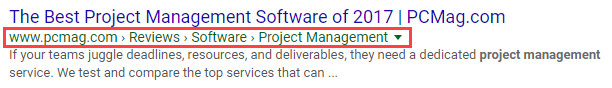
- Breadcrumb URL – Instead of displaying a page’s specific URL, Google replaces the URL with a breadcrumb trail. Have a developer add structured data markup to signify the navigation hierarchy for different pages of your site.
.
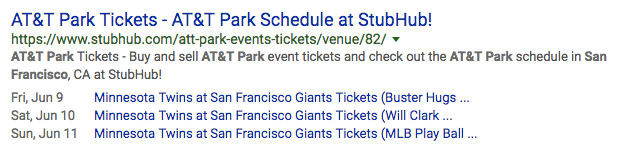
- Events – If your business hosts events regularly, event pages and listings can use structured data to earn upcoming event listings under search results.
.
If you want to try your hand at adding structured data without bringing in the development team, Google offers a structured data markup tool that makes it easy to markup individual pages.
5. Optimize for Featured Snippets
The best way to stand out in search results is by earning featured snippets. Featured snippets are expanded results that appear in position zero—above the number one result—for relevant queries. Often, featured snippets provide definitions, lists, or tables.
Featured snippets include a link to the page providing the information. They may also include a corresponding image, but the image and the snippet can come from two different sites.
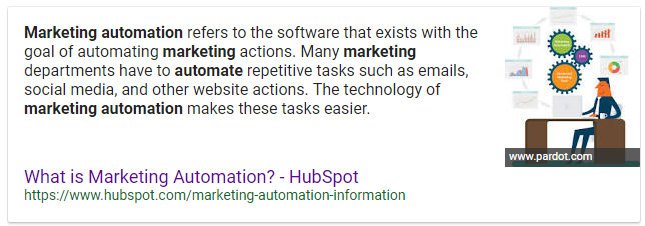
The definition of marketing automation comes from HubSpot, but the image is provided by Pardot.
In testing the impact of featured snippets, HubSpot found that earning a featured snippet increased CTRs by 114%, even when their natural ranking was the number one spot.
The best way to stand out in search results and improve organic click-through rates is to optimize content for featured snippets:
- Determine which keywords populate featured snippets by conducting a depersonalized search for targeted keywords. If a featured snippet appears, consider how you could create a better answer—clearer, more concise, or in more accessible language—in your content to overtake the featured snippet position.
- If there’s no featured snippet, it doesn’t mean Google doesn’t want one. In fact, the number of featured snippets that appear in search results has been growing each year. Consider the user intent of targeted keywords. Does it suggest that users are looking for a distinct answer—a definition, list of options, or step-by-step instructions? If so, provide that answer in your content, and you may generate a new featured snippet.
How to Stand Out in the SERPs
With compelling SEO titles, enticing meta descriptions, descriptive URLs, and expanded search results from structured data markup and featured snippets, you can stand out in the SERPs and improve organic click-through rates. This will lead to increased organic traffic, and it may even lead to higher rankings.
Get started by identifying underperforming pages. Conduct a search for the keywords that populate your result, and see if featured snippets appear. If so, take time to optimize content to overtake that featured snippet, and watch click-through rates soar.
What's Next?
Profound Strategy is on a mission to help growth-minded marketers turn SEO back into a source of predictable, reliable, scalable business results.
Start winning in organic search and turn SEO into your most efficient marketing channel. Subscribe to updates and join the 6,000+ marketing executives and founders that are changing the way they do SEO:
And dig deeper with some of our best content, such as The CMO’s Guide to Modern SEO, Technical SEO: A Decision Maker’s Guide, and A Modern Framework for SEO Work that Matters.






